Moxibustion, to correct a breech presentation of the fetus
Introduction
It has been estimated that the frequency of breech presentation is between 3 and 4% of all pregnancies that reach term (Hickok DE et al., 1992). It is associated with a greater risk of perinatal and neonatal mortality and morbidity. The risk can be reduced if it is possible to turn the fetus round by means of external cephalic version (ECV), which is achieved by placing the hands on the woman’s abdomen and applying external force. However, this procedure is not without risk and can only be performed in hospital. In the majority of cases a caesarean section is performed.
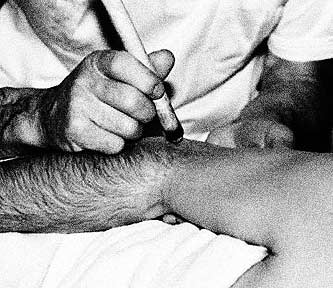
For thousands of years, the Chinese have used acupuncture to treat their ailments and, in cases of breech presentation, they practise moxibustion. Moxibustion is one of the techniques of traditional Chinese medicine which works by applying heat stimulation to the same points as those used in acupuncture. Heat is generated by burning a herb, artemisia vulgaris. The term is derived from the Japanese name for this herb – moxa. First the artemisia is pressed and dried and then it is rolled in paper mulberry which smoulders once lit.
Moxibustion is a technique that is simple, effective, safe and generally well tolerated by both mother and newborn. It is very cheap, easy to learn and can be practised by any health worker. In cases of breech presentation, together with external cephalic version, it may therefore be a useful alternative to a caesarean section.
Moxibustion is an integral part of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and is widely practised in China where it has been calculated that 500 million people use acupuncture.
In many European countries, in particular in England, France and Germany, moxibustion and acupuncture are treatments that are fully integrated into the respective national health services. These practices are also widespread in Italy, where many public and private centres offer this service to users and are conducting further studies on the efficacy of these methods.
The World Health Organisation lists breech presentation (Malposition of fetus, correction of) as one of the pathologies, symptoms or conditions for which the effectiveness of acupuncture (moxibustion) has been proven and controlled clinical trials.
The Jiangxi Women’s Hospital of Nanchang in the People's Republic of China, has done the most to publicise this method by means of a first randomised controlled clinical trial. The study was published in 1998 by J.A.M.A., the prestigious review of the American Medical Society. The work of scientific convalidation was coordinated by Professor Huang Weixin and Professor Francesco Cardini.
DOWNLOAD THE BROCHURE PDF
albanian (0.7 MB)english (0.4 MB)
spanish (0.4 MB)
serbian (0.9 MB)




 COUNTRY OF ORIGIN
COUNTRY OF ORIGIN